Using the exchange market data as the main instrument,
Elliott discovered that the ever-changing price configuration of the exchange
market shapes up a certain structured pattern, which describes the fundamental
natural harmony. On this discovery basis, he developed a rational market analysis
system.
Elliott pointed out the movement
patterns or «waves» emerging again and again in the market price movements and
they are self-similar in form, but not always in timeframe and amplitude. He
entitled these models, gave definitions and illustrations. Thereafter, he
described how these structures link together to form a zoomed version of these
models, and then how they link for building up the extended identical models
etc.
To be brief, the Wave Principle -
is a catalogue of price adjustments models and explanations of where is
most likely to see such figures in the market development process. Elliott
classifications represent themselves as a rule set for the market behaviour
explanation. Elliott posited about the prediction significantly of the Wave principle,
which was called after its developer's name.
Essential concepts
The main market cycle motion runs up according to
the structure consisting of a 5-wave sequence, which is corrected by a 3-wave
structure with the opposite direction (pic1).
 |
| Рiс. 1. Diagrammatic view of the Wave Principle |
«Enumerated phases» called by R.N. Elliott as «cardinal waves» now known as «impulsive waves». «Sideward phases» nowadays - «corrective waves» or sometimes just «triplets». Wave 2 corrects wave 1; wave 4 corrects wave 3. The full sequence of waves 1-5 is corrected by the a-b-c sequence. Looking at the large scale image the wave sequence 1-5 shapes up a higher level wave. Thus, 1-5 wave movement completes the wave, and, while a-b-c sequence completes the wave or (pic.2).
 |
| Pic.2 Schematic wave diagram |
In the microscale each wave at the pic.2 can be divided into small wave components:
- wave 2 corrects the wave 1;
- the wave 4 corrects wave 3;
- a-b-c sequence corrects the sequence of 1-5 waves (pic.3).
 |
| Pic.2a The EUR\USD pair graph |
At the pic.2a at the EUR\USD currency pair graph, we can see the Elliott full wave cycle. The main cycle waves are traced with the red line, yellow lines signal small wave components of the main waves.
 |
| Pic. 3 Wave fractionation into a small wave components |
There are three rules which are «unbreakable»:
- Wave 2 never turns back ["reverses»] further than wave 1. If the impulsive waves are up-directed, then wave 2 can not slide below the 1 wave's start point (see pic. 4). If the impulse the sequence goes down, the wave 2 can not surge above the peak, from which took It rises the wave 1.
- The wave 3 can not be the shortest among the «impulsive waves» (see pic.5). The wave 3 is not required to be the longest, but it almost always is.
- In the increasing sequence, wave 4 can not step out of the wave 1 peak range. In the falling sequence, the wave 4 rally can not tick above wave 1.
If even one of these rules is broken, the sequence
is not impulsive (pic.6).
Impulsive waves
In one of the waves, a variation may take place,
known as extension. Extension
— is exaggerated or overextended movements, which don't fit into the scale,
compared to other impulse waves. Take into account that extensions can be only
in one of the impulsive waves (in the 1st, 3d or 5th). More often
these extensions occur in the 3d wave. They can also emerge in the extended
wave.
 |
| Pic. 7. Sequence from (1) to (5) the wave 3 |
 |
| Pic. 8 Sequence from i to v - extended wave (3); it is the part of extended wave 3 |
There is one more impulsive waves variety - diagonal triangle, wedge-shaped structure, formed by two concurrent lines (in their normal form). Such structures may be witnessed in the wave 5 position, usually after a drastic and short-term motion of the previous wave 3. Usually, in such a wedge, the sub-waves have a «triplet» or «quintuplet» form. A crossover between the 1 and 4 wave endings — is also a frequently seen issue. It is the only well-known exception from Elliott's «noncrossing rule» of 1 and 4 waves.
An example is given in the pic.9
Diagonal triangles can also be found in the C wave
position, which is a part of the «sideward phase», i.e. in the corrective
waves. As well as in the case with wedges in the 5 wave position, these formations
signal the movement ends, one level above the considered one.
 |
| Pic.9. Wave 5 — diagonal triangle |
Betweentimes, the 5th wave is not able to overcome the previous wave 3 ending level. A concept with this meaning is negatively inspired - «failure». You can make sure of such structure existence if the internal waves of the «failed 5th wave» correspond to all three rules related to the impulse waves. Failure — is a reversal structure, which generated the «double tops» or «double lows» well known in classical chartism. This structure is rarely seen at the «minutes» or «minors», but it is widely spread at the «minutes» (pic.10).
CORRECTIVE WAVES
Movements, directed versus the trend are called
«corrective waves» or just «corrections» (retracements). Sometimes, they are
called «consolidations» or «lateral phase». The only and the most essential rule, which can be conceived
from different corrective patterns examination, is that the rollbacks can never
turn into «quintuplets». Only moving waves are the «quintuplets». For this reason, the starting 5-wave motion against the older wave level is never a
correction end, it is just a part of it.
Correctional processes are carried out
in two ways. Sharp kick-backs bend steeply versus the movement direction of the
older wave level. Although the sideward corrections always carry out the total
rollback from the preceding wave, usually they include a move to its starting
point or even out its bounds range, shaping up a lateral movement facade. The
separate corrective patterns break down into the main categories:
- Flats (3-3-5), (pic.12a-b)
 |
| Pic. 12a. Flat Bull correction |
 |
| Pic.12b. Flat Bear correction |
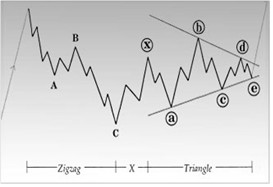
- Triangles (3-3-3-3), (pic. 13a-b)
 |
| Pic. 13a Triangle Bull correction |
 |
| Pic. 13b Triangle Bear correction |
The combination of This standard pattern constructs the 4th category.
- Double triplets and triple triplets (combined structures)
a) Composite corrective forms Double triplets
Flat-complex (pic.14a — e).
 |
| Pic. 14c. Zigzag- |-Х-| -Flat correction |
 |
| Pic.14d Flat correction- |-Х-| - Flat correction |
b) Composite corrective forms
Triple triplets (pic.15a-d)
 |
| Pic.15a. Zigzag-|-Х-|-Zigzag-|-Х-|-Zigzag |
 |
| Pic.15b Zigzag-|-Х-|-Flat correction- |-Х-|-Triangle |
 |
| Pic.15c. Flat correction-|-Х-|-Zigzag-|-Х-|-Triangle |
 |
| Pic.15d. Flat correction-|-Х-|-Flat correction-|-Х-|- Flat correction |
You must have already drawn attention to that the basic patterns in double and triple triplets are linked by wave X, which also turns out to be a triplet (corrective wave) and it may be a flat, zigzag and triangle.
Alternation Principle
Despite its sounding title, the alternation
principle — is exactly a principle, i.e. a valuable norm, but not a changeable rule in the Wave methods. The market experience shows that the principle is
valid during 90% of the time between the
waves 2 and 4 in
5-waves structure.
In the statement made by R.N.Elliott, the principle
requires the alternation in emerging of simple and composite correctional
structures in waves 2 and 4.
A simple deep correction (zigzags, double zigzags) in
the wave 2 must construct a composite sideward
one (flat, triangle, double and triple triplets) in wave 4.
However, in the Forex market, the Alternation principle
is rightful mostly concerning the extent, not the structure of the
corrections. For instance, if wave 2 rolls back by 61.8% or more from wave 1,
most likely that wave 4 would pull back by 38.2% or less from wave 3.
If wave 2 rushes back by 38.2% from wave 1, then
wave 4 will correct wave 3 by 23.6% or 50%. The opportunity of structure
alternation still remains, but from time to time there may emerge significant
exceptions. More often, the alternation
process comes about the extension or deepness of the corrections, rather than
about their structures and forms.
This principle also requires us to look for
different formations in double and triple triplets. In the double
triplet the most commonly used structure is a flat correction or zigzag.
If the triangle is shaping up, it almost always appears to be the last
structure in the correctional phase.
Two sequent flat corrections signal that
there will be the third one, ordinary — a triangle. A triple triplet may be
constructed from three flat corrections. The Theory reqiues to search in the
triangle different structures in tangent and integral subwaves. Subwave A is
not similar to subwave B; subwave B
differs from subwave C etc.
FIBONACCI RELATIONSHIPS
Elliott noticed in his work «Nature's Law» that
Fibonacci sequence is a small basis of the Wave Principle. Here are Fibonacci
figures: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610 etc.
The sum of any two neighbor figures is equal to the next figure in the
sequence. Example: 3 + 5 = 8; 5 + 8 = 13; 8 + 13 = 21; 13 + 21 = 34 etc.
Dividing of Fibonacci figure by the neighboring lesser one gives 1.618.
Example: 34/21=1.618. Further, the same
Fibonacci figure dividing by the next one gives 0.618. Example: 34/55 =
0.618. The figure opposite to 1.618 is
equal to 0.618.
Likewise, the contrary to 0.618 is 1.618. Example: 1 /0.618 =
1.618, и 1 / 1.618 = 0.618.
Dividing of any Fibonacci figure by the previous one by two positions in the
sequence increases the result to 2.618.
And this figure dividing by the next one, which is in two positions from
it in the sequence, amounts to 0.382.
Example: 55/144 = 0.382. A contrary
figure to 2.618 is 0.382, and the figure opposite to the proportion 0.382 is 2.618. Example: 1 /2.618 = 0.382; 1 /
0.382 = 2.618. Any Fibonacci figure dividing
by the figure which is 3 positions before it, gives 4.236. Example:
144/34 = 4.236. And the same figure diividing by the next one, 3 positions away
from it in the sequence, gives a reading of 0.236. Example: 144/610 = 0.236.
The opposite figure to 4.236 is equal to 0.236, and the figure opposite to the
proportion 0.236 is 4.236. Example: 1 /4.236 = 0.236; 1 / 0.236 = 4.236. A
proportion which equals to 1 (par) shows
the equality relation between first two
figures in the Fibonacci sequence; thus, 1/1 = 1. Relation 0.5 appears as the
second and third figures ratio in the sequence, therefore, 1/2 = 0.5.
Fibonacci figures don't have any value during the
market movements «extension» forecast regarding the absolute price value. The
key elements — relations between the sequence figures. More frequently and
reliable the Fibonacci figures can be seen between the alternating waves,
rather than between the neighboring.
As an example, the wave 3 length in the
5-wave structure is influenced mostly by the wave 1 length, rather than the
wave 2 length. The target orientators counted by means of Fibonacci
relationships usually turn out to be essential support or resistance levels,
even if after that follows their break through.
An important addition to
Elliott Wave Principle appears to be a comprehension that
Fibonacci proportions are the «initial determinants», measuring the price
«duration» through time in the market. Elliott Wave Principle provides us the
form and structure and Fibonacci relationships give an instrument for measuring
any price movement potential, including the limits of possible finishing
date of these movements. This a very powerful combination.
Let us look through more detailed how Fibonacci
ratios behave during the wave formation.
Impulse waves
The ending point of wave 3 — the hardest to
predict, compared to three impulse waves. As the 3rd wave may be shorter than
the 1st one (rather seldom), then its closing forecast — is a real trap for an imprudent analyst.
If it is shorter than wave 1, wave 3 may equal to
wave 1 or be longer by 1.618. In case of extensions, wave 3 may be longer even
by 2.618 and 4.236 than wave 1. The length of wave 5 can be obtained by means of
Fibo ratios, used for price movement between the opening of wave 1 and closing
of wave 3.
Extensions
In each 5-wave structure worth taking into account
that only one from the impulse waves (1st, 3d or 5th) will be
extended. If wave 3 is extended, then waves 1 and 5 have the equality tendency
on a price distance or equality tendency on movement length from the opening
point to the closing one.
In case of extension the middle of «wave 3 within
wave 3» usually points at the central point of all wave 3 movement. A
mysterious thing as extension still remains one of the least clear matter in
the Wave Principle. If we see a serie of overlapping waves in such wave
structure point, where is not considered a presence of horizontal and diagonal
triangles — usually it is an extension.
In Forex markets about 60% of extensions appear in three forms. Extended
5th waves can occur in 35% and left 5% - extended 1st
waves. If an extended wave is found in the first 5-wave structure, so the next
correction of all structure should be expected around wave 2, instead of
regular wave 4 range. It is especially correct in case when wave 5 is much less
than wave 3 in
the sequence.
Within the extensions the corrections are smoother.
A normal percentage of reversal against the previous wave is – 23.6%; the
corrections rarely exceed 38.2%. If wave 2 pulls back from the 1st
one less than by 50%, most probable is that wave 3 will be extended. Such
tendency becomes more possible if wave 2 structure is similar to flat and
irregular correction.
If wave 5
in any 5-wave structrure is extended, then about 80% of
cases this structure is wave 3
in larger formation. If wave 5 is extended — its length
is often bigger by 1.618 than the full
price distance between the wave 3 opening point and wave 3 peak. See the
picture below:
Methods used during the predictive modeling of
corrective waves deepness according to the Elliott Wave Principle may be
various, though the main approach to applies to multiplication of Fibo ratios
0.236, 0.382, 0.5 и 0.618 by the preceding impulse wave length.
The corrections have an inclination to price
reversion to the range of the previous wave 4, at lower rate — frequently, a
little bit further than its extremum. Elliott named 8 types of correctional
structures and found out that they can double or triple in the long-term lateral consolidations.
A double triplet —
the most complicated correctional structure within the Wave Principle. That is
almost the one and the most widespread reason for mistakes in the forecasts and
temporary targets. (pic.a — f). The double triplets are not frequently occured
in higher rate waves, however, it is not a rarity at 1-hour and 10-minutes
chats.
If the correction starts from a compound sideward structure (flat
correction or triangle), then the rollback from the dominating impulse trend
usually confines itself to the deepness of
38.2% or at the very outside - 50%. Generally, it is correct even if
this correction is wave 2. A
correction, which doesn't run beyond
38.2% of the previous motion signals the restraining power of the major trend.
Identically, a consolidation, requiring
time for closing, it is a curtain-raiser prior to the crush, which will take
place after the correctional structure ending. 50%-corrections in the 5-wave structures
— is an everyday occurence, but they happen not so often as 61.8%-corrections.
But 50%-corrections are frequent seen in the Rally internal waves taking place
in the bear market, i.e. inside the wave B in the zigzag. The end of zigzag
doesn't guarantee that the whole retracement has finished, as the «rollback»
forms may contain complicated structures.
But the analyst has to follow the
most straightforward explanation of completed structure. R.N.Elliott also
affirmed that the most simple structure often appears to be a correct
interpretation. Elliott did not try to give exact prediction rules for longer
correctional structures.
In «double zigzag» structures the secong zigzag must
close significantly lower than the bottom bound of the first one (in the bull
market). And, on the contrary, in the
falling market the second zigzag must close much higher than the first zigzag
peak.
The Wave Principle doesn't give an opportunity to
predict the wave 2 ending point. Unfortunately, even reliable Fibo ratios are useless.
Hereby, Elliott can offer only verisimilar points, where can be put the Stop
levels. That is why it's better to avoid trading in the second waves.
Oftener,
the second waves are simple (zigzag, double zigzag), and the fourth waves — are
complicated (flat retracement, irregular correction, triangles, double or
triple triplets etc.). Wave 2 usually «pulls back» deeper than the 4th
one. Wave 2 has a rollback trend to 61.8% or furhter against wave 1.
If that
does not happen — the next most likely reading is 50%. The most typical
rollback deepness of wave 4 equals to 38.2% from wave 3. In case of wave 5
«failure», can be expected that the next deepness retracement
will turn out to be the most possible for a
correctional structure.
 |
| Pic.17 demonstrates a typical rollback deepness of wave 2 |
 |
| Pic.18 demonstrates a typical rollback deepness of wave 4 |
Fibonacci correction levels are counstructed as follows. First of all, between two extreme points is traced out the trend line — for example, from the bay to the opposite top. After that, are designed 9 horizontal lines, crossing the trend line at Fibonacci levels: 0,0%, 23,6%, 38,2%, 50%, 61.8%, 100%, 161,8%, 261,8% и 423,6%. (Due to selected scale some of these lines may not fit at the graph).
After a strong rise or fall the prices often
reverse back, correcting a huge part of its origin movement. During such
reversal motion the prices frequently meet the support/resistance at Fibonacci
correction levels or around them.
Fibonacci proportions comprehension: the first
pullback level (23.6%) is usually insignificant, the next level (38.2%) - as a
rule, it is a substantial level, the market rolls back from it almost all the
timel; if the market reversal goes on afterwards — the next essential
consolidation level will be at 50%, and the pullback continuation to 61.8%
usually signals a final closing of the preceding trend.
Lessons:
- Operations With Trader Platform On The Basis Of Meta Trader 4
- Wave Analysis. Elliott Wave Principle